type
status
date
slug
summary
tags
category
icon
password
1、为什么需要树这种数据结构
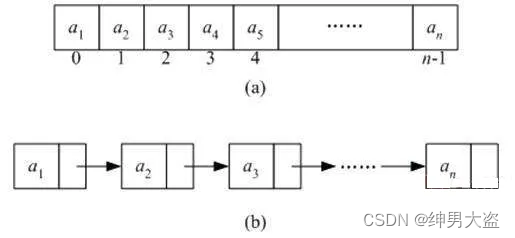
数组存储方式的分析优点:通过下标方式访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组,还可使用二分查找提高检索速度。缺点:如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按一定顺序)会整体移动,效率较低
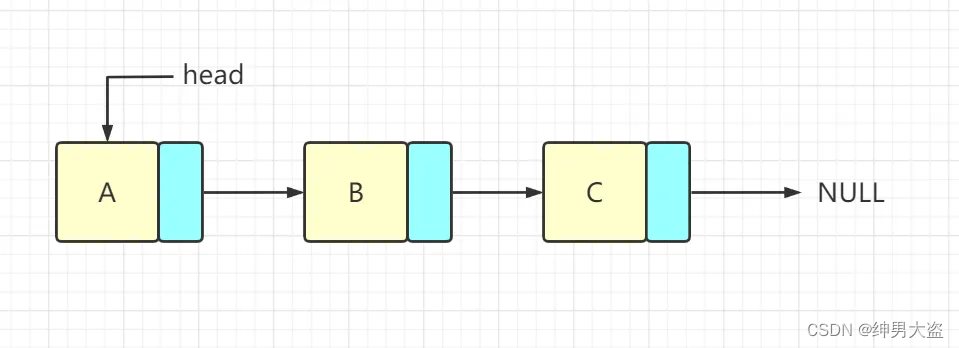
链式存储方式的分析优点:在一定程度上对数组存储方式有优化(比如:插入一个数值节点,只需要将插入节点,链接到链表中即可,删除效率也很好)。缺点:在进行检索时,效率仍然较低,比如(检索某个值,需要从头节点开始遍历)
树存储方式的分析能提高数据存储,读取的效率, 比如利用 二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),既可以保证数据的检索速度,同时也可以保证数据的插入,删除,修改的速度
。
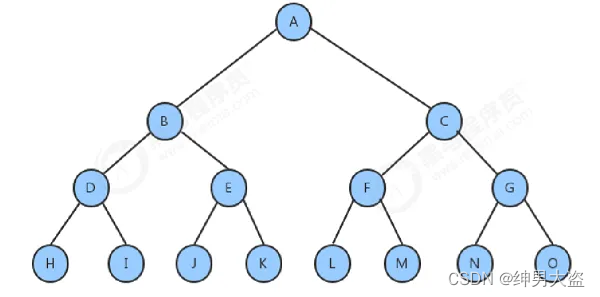
2、树示意图
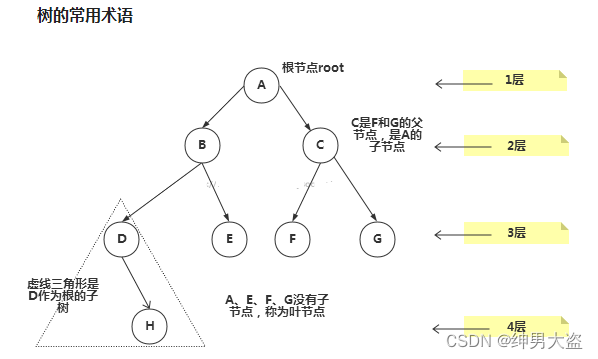
树的常用术语(结合示意图理解):
- 节点
- 根节点
- 父节点
- 子节点
- 叶子节点 (没有子节点的节点)
- 节点的权(节点值)
- 路径(从root节点找到该节点的路线)
- 层
- 子树
- 树的高度(最大层数)
- 森林 :多颗子树构成森林
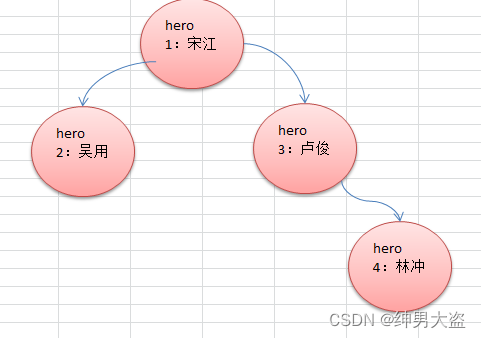
3、二叉树的概念
- 树有很多种,每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树。
- 二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点。
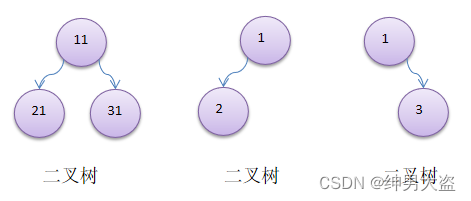
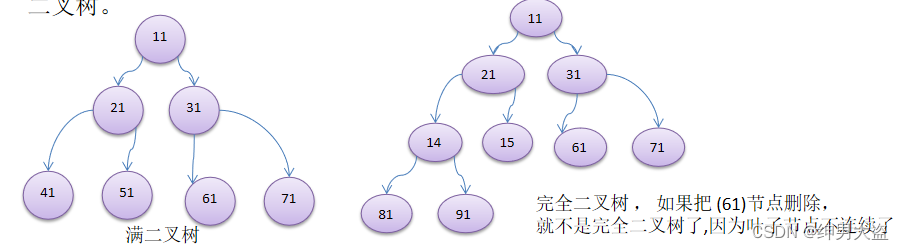
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且结点总数= 2^n -1 , n 为层数,则我们称为满二叉树。
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树。 使用前序,中序和后序对下面的二叉树进行遍历.
前序遍历: 先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树 中序遍历: 先遍历左子树, 再输出父节点,再遍历右子树 后序遍历: 先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点 小结: 看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前序,中序还是后序
4.1、前序遍历
4.2、中序遍历
4.3、后序遍历
5、二叉树-查找指定节点
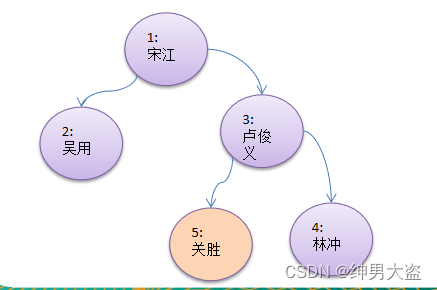
要求
请编写前序查找,中序查找和后序查找的方法。
并分别使用三种查找方式,查找 heroNO = 5 的节点
并分析各种查找方式,分别比较了多少次
5.1、前序查找
5.2、中序查找
5.3、后序查找
6、二叉树-删除节点
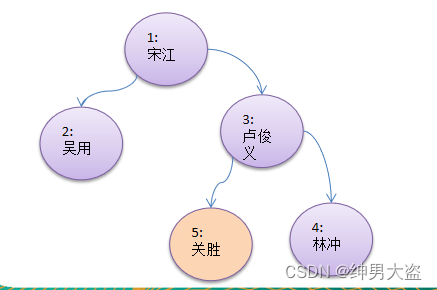
要求:
如果删除的节点是叶子节点,则删除该节点如果删除的节点是非叶子节点,则删除该子树.测试,删除掉 5号叶子节点 和 3号子树.
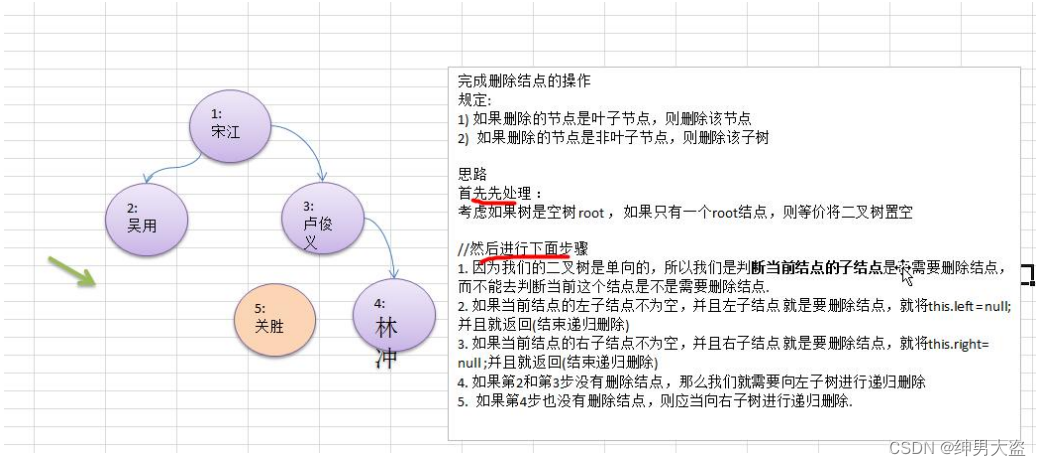
6.1、删除节点思路分析
7、代码实现
- 作者:IT小舟
- 链接:https://www.codezhou.top/article/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91
- 声明:本文采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处。