type
status
date
slug
summary
tags
category
icon
password
1、先看一个需求
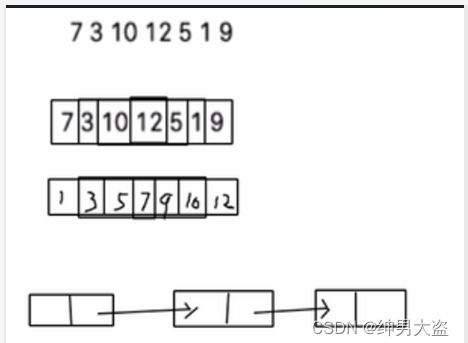
给你一个数列 (7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9),要求能够高效的完成对数据的查询和添加。
1.1、解决方案分析
使用数组 数组未排序, 优点:直接在数组尾添加,速度快。 缺点:查找速度慢. [示意图] 数组排序,优点:可以使用二分查找,查找速度快,缺点:为了保证数组有序,在添加新数据时,找到插入位置后,后面的数据需整体移动,速度慢。[示意图]
使用链式存储-链表 不管链表是否有序,查找速度都慢,添加数据速度比数组快,不需要数据整体移动。[示意图]
使用二叉排序树
2、二叉排序树介绍
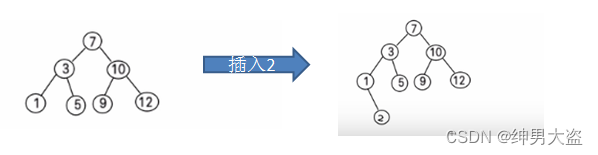
二叉排序树:BST: (Binary Sort(Search) Tree), 对于二叉排序树的任何一个非叶子节点,要求左子节点的值比当前节点的值小,右子节点的值比当前节点的值大。 特别说明:如果有相同的值,可以将该节点放在左子节点或右子节点
比如针对
前面的数据 (7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9) ,对应的二叉排序树为
:
3、二叉排序树创建和遍历
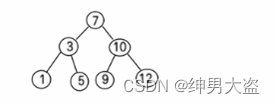
一个数组创建成对应的二叉排序树,并使用中序遍历二叉排序树,比如: 数组为 Array(7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9) , 创建成对应的二叉排序树为 :
3.1、代码实现
- 作者:IT小舟
- 链接:https://www.codezhou.top/article/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%A0%91
- 声明:本文采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处。

