type
Post
status
Published
date
May 24, 2023
slug
希尔排序
summary
希尔排序
tags
数据结构和算法
category
技术分享
icon
password
希尔排序 java详细讲解
1、希尔排序法介绍
希尔排序是希尔(Donald Shell)于1959年提出的一种排序算法。希尔排序也是一种插入排序,它是简单插入排序经过改进之后的一个更高效的版本,也称为缩小增量排序。
2、希尔排序法基本思想
希尔排序是把记录按下标的一定增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序;随着增量逐渐减少,每组包含的关键词越来越多,当增量减至1时,整个文件恰被分成一组,算法便终止
3、简单插入排序存在的问题
我们看简单的插入排序可能存在的问题.
数组 arr = {2,3,4,5,6,1} 这时需要插入的数 1(最小), 这样的过程是:
{2,3,4,5,6,6}
{2,3,4,5,5,6}
{2,3,4,4,5,6}
{2,3,3,4,5,6}
{2,2,3,4,5,6}
{1,2,3,4,5,6}
结论: 当需要插入的数是较小的数时,后移的次数明显增多,对效率有影响.
4、希尔排序法的示意图
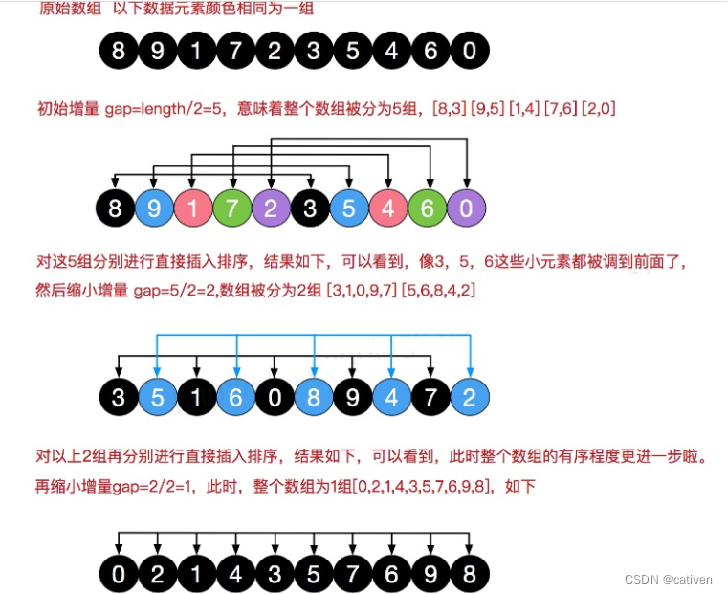


5、希尔排序法应用实例:
有一群小牛, 考试成绩分别是 {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0} 请从小到大排序. 请分别使用
希尔排序时, 对有序序列在插入时
采用交换法
, 并测试排序速度.
希尔排序时, 对有序序列在插入时
采用移动法
, 并测试排序速度

6、代码实现(交换法)
7、代码实现(交换法简化)
8、代码实现(移动法简化)
如有不正确的还请支出,谢谢!!!